Spring Boot CRUD Application using Thymeleaf and Spring Data JPA. In this article, we will learn how to create a Spring Boot CRUD Application with thymeleaf. To know How to perform CRUD application using REST API in spring boot check this article https://codebun.com/crud-operation-in-spring-boot-using-restapi/
As we know, while creating a web application we need to perform some operations that are common in every application such as CREATE, READ, UPDATE and DELETE. So, we will take a look at how to create a CRUD Application in Spring boot using Thymeleaf.
We will be following the Spring Boot Architecture. At the View layer, the Thymeleaf template will be used. Spring Data JPA is used at the Data access layer.
CRUD operation in Spring boot with Thymeleaf template
- Create a Spring Boot Starter Project.
- Create a package structure
- Create a database in MYSQL
- Configure application. properties file.
- Create an Entity
- Create a Repository i.e the Data Access Layer.
- Create Service Layer.
- Create Controller.
- Create Views using Thymeleaf.
Spring Boot CRUD Application using Thymeleaf and Spring Data JPA
In the below example, let’s create a simple spring boot application using the thymeleaf template and Spring Data JPA at the data access layer.
Create a Project
Step 1: Open IDE STS- Spring Tool Suite
Step 2: Go to File > Spring Starter Project.

Step 3: Now, Fill all the fields as shown below and click Next.

Step 4: Now, Add the dependencies as per your requirement, I have added Spring Web Dependency and Spring Data JPA, Thymeleaf, and etc. click Next > Finish.

Now, wait for some time and your project structure will be ready. Go to the pom.xml file and you will see the following dependencies will be added automatically.
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
Once the project is created, create the folder structure as shown below
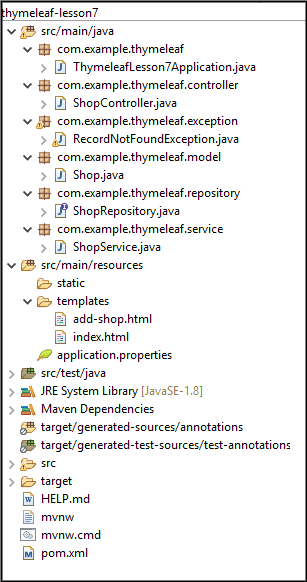
Create Database
mysql> create database db_demo;
Configure application. properties file
This is the file provided by spring boot to configure JDBC URL, username, password, and driver class name. Also, configure JPA-related information.
# change the port server.port=8888 #Database Configrations spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_demo spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root spring.jpa.database-platform = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect spring.jpa.generate-ddl=true spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
- spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto is set to update so that whatever changes we do would be reflected in the schema.
- spring.datasource.url is used to set the URL of the MYSQL DB.
- spring.datasource.username is used to set the username and spring. datasource. password is used to set the password.
- spring.datasource.driver-class-name is used to set the driver class name.
- spring.jpa.show-sql is set to true to show SQL generated by the Hibernate.
- spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect is used to generate better SQL for the chosen database.
- spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql is set to true to format SQL queries.
- server.port is set to 8888.
Create a Model Class
Here, we will create an Entity that would be mapped to the database tables. It is nothing but the Java POJO class.
Shop.java
package com.example.thymeleaf.model;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
@Entity
@Table(name = "shop")
public class Shop {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String ownerName;
private long shopNo;
private String shopType;
private String address;
private String country;
}
- @Entity is used to annotate the classes to indicate that they are JPA entities.
- @Table annotation is used to specify the name of the table that should be mapped with entities.
- @Id annotation is used for the primary key.
- I have used the Lombok library to remove boilerplate code. In case you want to know what is Lombok check this article https://codedec.com/tutorials/how-to-configure-lombok-into-eclipse/
Create Repository Interface
The repository here is the DAO layer, which performs all the database operations. ShopRepository interface is created which will extends CrudRepository<ClassName, ID>
ShopRepository.java
package com.example.thymeleaf.repository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.example.thymeleaf.model.Shop;
@Repository
public interface ShopRepository extends CrudRepository<Shop, Integer> {
}
Create a Service Layer
This layer is responsible to handle business logic. Here, we will create the ShopService.
package com.example.thymeleaf.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.thymeleaf.exception.RecordNotFoundException;
import com.example.thymeleaf.model.Shop;
import com.example.thymeleaf.repository.ShopRepository;
@Service
public class ShopService {
@Autowired
private ShopRepository repository;
/*
* TODO: Get the List of Shops
*/
public List<Shop> getAllShops(){
List<Shop> list = (List<Shop>)repository.findAll();
return list;
}
/*
* TODO: Get Shop by Id.
*/
public Shop getShopById(Integer id) throws RecordNotFoundException {
Optional<Shop> shop = repository.findById(id);
if(shop!=null) {
return shop.get();
}
else
{
throw new RecordNotFoundException("Not found");
}
}
/*
* TODO: Save into db
*/
public Shop saveOrUpdateShop(Shop shop) {
if(shop.getId() == null) {
return repository.save(shop);}
else {
Optional<Shop> sOptional = repository.findById(shop.getId());
if(sOptional!=null) {
Shop shop2 = sOptional.get();
shop2.setOwnerName(shop.getOwnerName());
shop2.setAddress(shop.getAddress());
shop2.setShopType(shop.getShopType());
shop2.setCountry(shop.getCountry());
shop2.setShopNo(shop.getShopNo());
shop2 = repository.save(shop2);
return shop2;
}
else {
shop = repository.save(shop);
return shop;
}
}
}
public void deleteShop(Integer id) {
repository.deleteById(id);
}
}
- First, inject the ShopRepository interface using Autowiring.
- The business logic to CREATE, UPDATE, DELETE, READ is written inside this Service class.
Create a Controller
The request for the web pages will be handle by the handler methods in the controller class using @GetMapping.
ShopController.java
package com.example.thymeleaf.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.example.thymeleaf.exception.RecordNotFoundException;
import com.example.thymeleaf.model.Shop;
import com.example.thymeleaf.service.ShopService;
@Controller
public class ShopController {
@Autowired
private ShopService service;
@GetMapping("/")
public String home(Shop shop, Model model) {
List<Shop> list = service.getAllShops();
model.addAttribute("list", list);
return "index";
}
@GetMapping("/add")
public String showAddForm(Shop shop, Model model) {
return "add-shop";
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public String create(Shop shop, Model model) {
service.saveOrUpdateShop(shop);
return "redirect:/";
}
@RequestMapping(path = { "/update","/update/{id}"})
public String update(Model model,@PathVariable("id") Integer id) throws RecordNotFoundException {
if(id!=null) {
Shop shop2 = service.getShopById(id);
model.addAttribute("shop", shop2);
}else {
model.addAttribute("shop", new Shop());
}
return "add-shop";
}
@RequestMapping(path = { "/delete/{id}"})
public String delete(Model model, @PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
service.deleteShop(id);
return "redirect:/";
}
}
- @Controller annotation marks the ShopController class a Request Handler.
- Every request coming for the ‘/’ URL will be handled by the home() method. It would redirect you to the index page.
- @GetMapping is used to map HTTP GET requests to a handler method.
- @PostMapping is used to map HTTP POST requests to a handler method.
- @PathVariable annotation is used to extract values from request URI as shown below.

Create an Exception Class
If the resource is not found this exception will be thrown.
package com.example.thymeleaf.exception;
public class RecordNotFoundException extends Exception {
public RecordNotFoundException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
Create View using Thymeleaf
Go to src/main/resources/template folder and create an index.html file. Now inside the index.html file make sure to add the following code:
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.1.0/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-KyZXEAg3QhqLMpG8r+8fhAXLRk2vvoC2f3B09zVXn8CA5QIVfZOJ3BCsw2P0p/We" crossorigin="anonymous">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@popperjs/core@2.9.3/dist/umd/popper.min.js" integrity="sha384-eMNCOe7tC1doHpGoWe/6oMVemdAVTMs2xqW4mwXrXsW0L84Iytr2wi5v2QjrP/xp" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.1.0/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-cn7l7gDp0eyniUwwAZgrzD06kc/tftFf19TOAs2zVinnD/C7E91j9yyk5//jjpt/" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/4.7.0/css/font-awesome.min.css">
<title>CRUD</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5">
<h2 align="center">CRUD using Thymeleaf Template</h2>
<p align="center"><a th:href="@{/add}" class="btn btn-info">Add a Shop</a></p>
<table class="table table-bordered table-sm">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Owner Name</th>
<th>Shop Type</th>
<th>Shop Number</th>
<th>Address</th>
<th>Country</th>
<th>Action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="l : ${list}" th:field="${l}">
<td th:text="${lStat.index+1}"></td>
<td th:text="${l.ownerName}"></td>
<td th:text="${l.shopType}"></td>
<td th:text="${l.shopNo}"></td>
<td th:text="${l.address}"></td>
<td th:text="${l.country}"></td>
<td>
<a th:href="@{/update/{id}(id=${l.id})}" ><i class="fa fa-edit" ></i></a>
<a th:href="@{/delete/{id}(id=${l.id})}" ><i class="fa fa-remove"></i></a>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Here, the th: each attribute is used to iterate over the list of shops. The model attribute is accessed using ${} notation.
There is a complete article on how to iterate list https://codebun.com/iterate-list-in-thymeleaf-using-spring-boot/

Create another view to add a shop called add-shop.html page inside src/main/resources/template folder.
- The name of the object model is in th:field=”*{}” attribute.
- In thymeleaf, the @ denotes the page context.
- In order to access the model object, we have to use ${} notation in thymeleaf.
- The th: object attribute is used to get the model object sent from the controller side.
add-shop.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.1.0/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-KyZXEAg3QhqLMpG8r+8fhAXLRk2vvoC2f3B09zVXn8CA5QIVfZOJ3BCsw2P0p/We" crossorigin="anonymous">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@popperjs/core@2.9.3/dist/umd/popper.min.js" integrity="sha384-eMNCOe7tC1doHpGoWe/6oMVemdAVTMs2xqW4mwXrXsW0L84Iytr2wi5v2QjrP/xp" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.1.0/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-cn7l7gDp0eyniUwwAZgrzD06kc/tftFf19TOAs2zVinnD/C7E91j9yyk5//jjpt/" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/4.7.0/css/font-awesome.min.css">
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Add Shop</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5">
<div class="card" style="width: 55rem; ">
<div class="card-header text-center bg-info ">
<h5>Add Shop</h5>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<form th:action="@{/save}" method="post" th:object="${shop}">
<input type="hidden" id="id" th:field="*{id}">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Owner Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" th:field="*{ownerName}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Shop Type</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" th:field="*{shopType}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Shop Number</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" th:field="*{shopNo}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Address</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" th:field="*{address}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Country</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" th:field="*{country}">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group text-center">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Add</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
There is a complete article on how to create a registration form https://codebun.com/registration-form-in-thymeleaf-with-spring-boot/

Run the Application
Now, Run the ThymeleafLessonApplication and Go to localhost:8888 and see the following output.

In this way, we learned how to create a Spring Boot CRUD Application using Thymeleaf and Spring Data JPA.
