Write a java program using Hashmap (Employees & Designations). A Company wants to obtain employees of a particular designation. You have been assigned as the programmer to build this package. You would like to showcase your skills by creating a quick prototype. The prototype consists of the following steps:
- Read Employee details from the User. The details would include the name and designation in the given order. The datatype for name and designation is the string.
- Build a hashmap that contains the name as key and designation as value.
- You decide to write a function obtainDesignation which takes the hashmap and designation as input and returns a string list of employee names who belong to that designation as output.
- Include this function in class UserMainCode. Display employee name’s in ascending order.
Input and Output Format:
- Input consists of employee details. The first number indicates the size of the employees. The next two values indicate the employee name employee designation. The last string would be the designation to be searched.
- Output consists of array values containing employee names.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications:
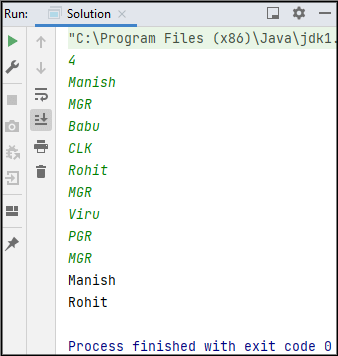
Sample Input 1:
4
Manish
MGR
Babu
CLK
Rohit
MGR
Viru
PGR
MGR
Sample Output 1:
Manish
Rohit
Java program using Hashmap (Employees & Designations)
Following are the steps to solve a problem using HashMap:
- First, input the size of a map. Create an empty LinkedHashMap to store value in key-value pair. Add the employee’s name and designation to the LinkedHashMap. Now, input the designation that should be searched. Pass them to dis() method.
- Create one more instance of LinkedHashMap to store the result.
- Inside the method, Create an empty LinkedHashMap. Now get all the keys from the map iterate over them and compare it with the designation which is passed. If the match is found associate the specified value with the specified key in the map and return the map.
- At last, iterate over the map and print the key i.e name.
package com.demo;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//Input the size of employees
int k1 = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
//Create empty LinkedHashMap and add employee name as key and designation as value
LinkedHashMap<String, String> hm = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < k1; i++) {
String k = sc.nextLine();
String s = sc.nextLine();
hm.put(k, s);
}
//Input the designation that needs to be searched
String n = sc.nextLine();
//to store the updated result
LinkedHashMap<String, String> hm1 = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
//Pass both map and designation that should be searched
hm1 = dis(hm, n);
//get all the keys
Iterator<String> it = hm1.keySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
//return the next elements in the iteration
String s2 = it.next();
//Printing the name of an employee i.e 'key'
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
public static LinkedHashMap<String, String> dis(LinkedHashMap<String, String> h1, String n) {
//Create an empty LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap<String, String> hm1 = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
//get all the keys
Iterator<String> it = h1.keySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
//return the next element in the iteration
String s2 = it.next();
//Returns the value(designation) to which the specified key is mapped
String s3 = h1.get(s2);
//compare both and if the designation(value) is matched then add them to an empty LinkedHashMap
if (s3.equals(n)) hm1.put(s2, s3);
}
return hm1;
}
}
Output
Thus, in this way, we learn how to solve a problem using Hashmap in Java.
