Write a program to read two strings and one int value(N). Check if the Nth character of the first String from the start and the Nth character of the second string from the end is the same or not. If both are the same return true else return false.
Note: Check need not be Case sensitive.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of two strings and an integer.
- The output consists of TRUE / FALSE.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
AAAA
abab
2
Sample Output 1:
TRUE
Java Program of String Processing
Following are the step to perform string processing:
- Input two strings and one integer value from the user.
- Pass them to lengthiestString() method.
- Inside the method, declare a variable ‘a’ of type boolean and set it as false.
- Now, get the nth character from the first input string and get the last nth character of the second string from the end and store it in variables c and d.
- Now, convert both of them into strings and compare them. If both are equal then set variable ‘a’ true else false.
- At last, return the value in the ‘a’ variable.
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1 = sc.nextLine();
String s2 = sc.nextLine();
int n = sc.nextInt();
boolean b = lengthiestString(s1, s2, n);
if (b == true) {
System.out.print("TRUE");
} else {
System.out.print("FALSE");
}
}
public static boolean lengthiestString(String s1, String s2, int n) {
boolean a = false;
char c = s1.charAt(n);
char d = s2.charAt(s2.length() - n);
String s3 = Character.toString(c);
// System.out.println(s3);
String s4 = Character.toString(d);
// System.out.println(s4);
if (s3.equalsIgnoreCase(s4)) {
a = true;
} else {
a = false;
}
return a;
}
}
Output
Write a Java program to String Processing – II
Write a program to read a string where all the lowercase ‘x’ chars have been moved to the end of the string. The return type is the modified string.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of a string.
- The output consists of a string.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
xxhixx
Sample Output 1:
hixxxx
Sample Input 2:
XXxxtest
Sample Output 2:
XXtestxx
Following are the steps to process string in Java:
- Input a string from the user.
- Next, use the replaceAll() method and remove all lowercase ‘x’ from the string and store it in s1. Next, remove all characters leaving lowercase ‘x’ and store it in s2.
- At last, concatenate both s1 and s2.
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.next();
String s1 = s.replaceAll("[x]", "");
String s2 = s.replaceAll("[^x]", "");
System.out.println(s1 + s2);
}
}
Output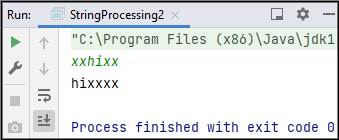
Write a Java program to String Processing – III
Write a program to read a string and also a number N. Form a new string starting with the 1st character and with every Nth character of the given string. Ex – if N is 3, use chars 1, 3, 6, … and so on to form the new String. Assume N>=1.
The return type is the string as per the problem statement.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of a string and integer.
- The output consists of a string.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
HelloWorld
2
Sample Output 1:
HelWrd
Following are the steps to process string in Java:
- Input a string and integer value from the user.
- Create an empty string buffer to hold the updated(result) string.
- First, replace all the whitespace with no space and store it in s2. Next, get the first character from variable s2 and append it to the string buffer.
- Now, use the for loop and start the index from last ‘n-1’ and for each iteration get a character from it and append it to the string buffer object.
- Repeat the above step till the whole string in s2 is traversed.
- At last, just print the value of the string buffer.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String s1=sc.nextLine();
int n=sc.nextInt();
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
String s2=s1.replaceAll(" ","");
sb.append(s2.charAt(0));
//System.out.println(sb);
for(int i=n-1;i<s2.length();i=i+n)
{
sb.append(s2.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output
Write a java program to String Processing – IV (String Processing – MixMania)
Write a program to read a string and check if it starts with ‘_ix’ where ‘_’ is anyone char(a-z, A-Z, 0-9).
If a specified pattern is found return true else false. The return type is TRUE / FALSE.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of a string.
- Output consists of TRUE / FALSE.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
Mix Mania
Sample Output 1:
TRUE
Following are the steps to process string in Java:
- Input string from the user.
- Create an empty string buffer.
- Get the first three characters from the input string using the subString() method and store them in variable s2.
- Declare and initialize variables a, b and c to 0.
- Now, extract the character from the 0th position from string s2 and store it in the ‘c21’ variable. Next, check if it is a digit or letter then assign 1 to variable a.
- Now, compare the value of ‘a’ with 1. If both are equal, then get the character from the 1st and 2nd position from string s2 and store it in c1 and c2.
- If c1is equal to ‘i’ then, assign 1 to b. If c2 is equal to ‘x’ then, assign c to 1.
- At last, check if all a,b, and c variable value is 1, then print true else false. it means the second character is ‘i’ and third is ‘x’.
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1 = sc.nextLine();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String s2 = s1.substring(0, 3);
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
char c21 = s2.charAt(0);
if (Character.isDigit(c21) || Character.isLetter(c21)) {
a = 1;
}
if (a == 1) {
char c1 = s2.charAt(1);
char c2 = s2.charAt(2);
if (c1 == 'i') {
b = 1;
}
if (c2 == 'x') {
c = 1;
}
}
if (a == 1 && b == 1 && c == 1) {
System.out.print("true");
} else {
System.out.print("false");
}
}
}
Output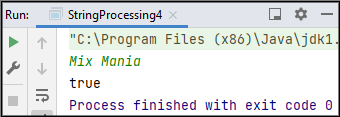
Write a java program to String Processing – V
Write a program to read a string and return a new string where the first and last chars have been interchanged.
The return type is the modified string.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of a string.
- The output consists of string.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
HelloWorld
Sample Output 1:
delloWorlH
Following are the steps to process string in Java:
- Input a string from the user.
- Create an empty string buffer and perform the below mention operation:
- Get the character from the 0th(start position) index and store it in variable ‘c’.
- Get the substring from 1st position to second last character and store it in variable ‘s2’.
- Next, get the last character from the input string and store it in variable ‘c1’.
- Append all the characters in variable ‘c’ to ‘s2’ and ‘c1’ to StringBuffer.
- At last, print the value in a string buffer.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1 = sc.nextLine();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
char c = s1.charAt(0);
String s2 = s1.substring(1, s1.length() - 1);
char c1 = s1.charAt(s1.length() - 1);
sb.append(c1).append(s2).append(c);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output
Write a java program to String Processing – VI(Strings Processing – Replication)
Write a program to read a string and also a number N. Return the replica of the original string for n given time.
The return type is the string based on the problem statement.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of a string and integer.
- The output consists of a string.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
Lily
2
Sample Output 1:
LilyLily
Following are the steps to process string in Java:
- Input a string and integer value from the user.
- Pass both of them to validString() method.
- Inside the method, create an empty string buffer. Use for loop and iterate over the string and append a string to itself in the number of times the user has given in the input integer value.
- At last, just print the value of the string buffer.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String s=sc.next();
int n=sc.nextInt();
String s2=validString(s,n);
System.out.println(s2);
}
public static String validString(String s,int n){
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
sb.append(s);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
Output
Write a java program to String Processing – VII
Write a program to read a string array, concatenate the array elements one by one separated by the comma and return the final string as output.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of an integer n which is the number of elements followed by n string values.
- The output consists of the string.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
3
AAA
BBB
CCC
Sample Output 1:
AAA,BBB,CCC
Following are the steps to process string in Java:
- Input integer value ‘n’ from the user.
- Create an array of strings of size n. Add elements to an array.
- Create an empty string buffer to hold the updated string.
- Now, iterate over the array of string and append ‘,'(comma) after every index position. Repeat this step till the whole array is traversed.
- At last, after iterating just remove the extra comma(‘,’) at the end of the string in the string buffer and print the value in the string buffer object.
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String s1[] = new String[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
s1[i] = sc.next();
}
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
for(int i=0;i<s1.length;i++)
{
sb.append(s1[i]).append(",");
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output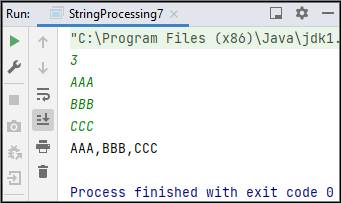
Write a java program to String Processing – VIII(String Processing – Username)
Write a program to read a valid email id and extract the username. The return type is the modified string.
Note – username is the string appearing before @ symbol.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of a string.
- Output consists of a string.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
admin@xyz.com
Sample Output 1:
admin
Following are the steps to find a username from a valid email string:
- Input email Id from the user.
- Pass it to the getvalues() method.
- Inside the method, First, use the string tokenizer to break the string into tokens by separating it with the ‘@’ symbol.
- Now, just get the first token by calling the nextToken() method and store it in variable s2.
- At last, print the value in variable s2.
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class FindUserName {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1 = sc.nextLine();
getvalues(s1);
}
public static void getvalues(String s1) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(s1, "@");
String s2 = st.nextToken();
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
Output
Write a java program to String Processing – XI.
Write a program to read a string and return a new string that is made of every alternate character starting with the first character. For example, New York will generate Nwok, and Samurai will generate Smri.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of a string.
- The output consists of a string.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
Hello
Sample Output 1:
Hlo
Following are the steps to create a string that is made up of every alternate character:
- Input a string from the user.
- Pass the string to the alternateChar() method.
- Inside the method, first, replace all the whitespace with no space.
- Next, create an empty string buffer to hold an updated string. Now, iterate over the string, increment index for every alternate position and get each character and append it to the string buffer.
- At last, just covert the string buffer to string and print them.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(alternatingChar(s));
}
public static String alternatingChar(String s)
{
String s1=s.replaceAll(" ", "");
StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length() ; i=i+2)
{
sbf.append(s.charAt(i));
}
String str = sbf.toString();
return str;
}
}
Output
Write a java program to String Processing – X.
Write a program to read a string and also a number N. Form a new string made up of n repetitions of the last n characters of the String. You may assume that n is 1 and the length of the string.
The return type is the string as per the problem statement.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of a string and integer.
- Output consists of a string.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
Hello
2
Sample Output 1:
lolo
Sample Input 2:
Hello
3
Sample Output 2:
llollollo
Following are the steps to perform string processing:
- Input string an integer value ‘n1’ from the user.
- Pass both of them to the formattingfOfString() method.
- Inside the method, create an empty string buffer. Now, iterate over the string and get the substring from the input value ‘n1’ to the length of the string.
- Append it to string buffer for every iteration.
- At last, convert it into a string object using the toString() method and return.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1=sc.nextLine();
int n1=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(formattingOfString(s1,n1));
}
public static String formattingOfString(String s1, int n1)
{
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0 ; i < n1 ; i++)
sb.append(s1.substring(s1.length()-n1, s1.length()));
return sb.toString();
}
}
Output
Thus, in this way, we can process strings in Java using multiple ways.
