Write a code to read two int array lists of size 5 each as input and to merge the two ArrayList, sort the merged array list in ascending order and fetch the elements at 2nd, 6th and 8th index into a new ArrayList and return the final ArrayList.The return type is an ArrayList with elements from 2,6 and 8th index
The return type is an ArrayList with elements from the 2,6 and 8th index positions. Array index starts from position 0.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of two array lists of size 5.
- The output is an array list.
Note – The first element is at index 0.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input 1:
3
1
17
11
19
5
2
7
6
20
Sample Output 1:
3
11
19
Sample Input 2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Sample Output 2:
3
7
9
Array List Merging and Sorting in Java
Following are the steps we will use to merge and sort ArrayList:
- Create three array lists of integer types.
- Add elements to two lists.
- Now, call the answer() method of Main1 class with both the array list.
- Now, we will add the element of the second list to the first by using the addAll() method.
- Just create one more list, and get the element from the specified position from the first list and add it to the newly created list. And return it.
- At last, just iterate over it and get all the elements.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<Integer> al1=new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> al2=new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
al1.add(sc.nextInt());
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
al2.add(sc.nextInt());
ans=Main1.answer(al1,al2);
//System.out.println(ans);
for(int k=0;k<3;k++)
System.out.println(ans.get(k));
}
}
class Main1 {
public static ArrayList<Integer> answer (ArrayList<Integer> al1, ArrayList<Integer> al2)
{
al1.addAll(al2);
Collections.sort(al1);
ArrayList<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<Integer>();
ans.add(al1.get(2));
ans.add(al1.get(6));
ans.add(al1.get(8));
return ans;
}
}
Output

Merge ArrayList with duplicates
Write a code to merge the array list element with duplicates. Here, we will use the addAll() method.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of two array lists of size 5.
- The output is an array list.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input:
3
1
2
6
5
6
9
6
7
4
Sample Output:
[3, 1, 2, 6, 5, 6, 9, 6, 7, 4]
Program to Merge ArrayList in Java
Following are the steps to merge the array list:
- Create two empty array lists.
- Add elements to each list.
- Use the addAll() method to merge one list to another.
- At last, print the list of elements from the first list.
package com.company;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayListProgram1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<Integer> al1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> al2 = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i =0 ;i <5;i++)
al1.add(scanner.nextInt());
for(int j =0 ;j <5;j++)
al2.add(scanner.nextInt());
al1.addAll(al2);
System.out.println(al1);
}
}
Output

Merge ArrayList without duplicates
Write a code to merge the array list element without duplicates.
Input and Output Format
- Input consists of two array lists of size 5.
- The output is an array list.
Refer sample output for formatting specifications
Sample Input:
3
1
2
3
3
2
5
6
7
8
Sample Output:
[3, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8]
Program to Merge ArrayList without duplicates in Java
Here, we can use LinkedHashSet to store unique values as well as to maintain insertion order. Following are the steps to merge the array list:
- Create two empty Array List.
- Add an element to each list.
- Create a LinkedHashSet and add the ArrayList and add all the elements of the second list to the set using the addAll() method.
- Now just create a resultant array list to store the set value and print it.
package com.company;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class ArrayListProgram1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<Integer> al1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> al2 = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i =0 ;i <5;i++)
al1.add(scanner.nextInt());
for(int j =0 ;j <5;j++)
al2.add(scanner.nextInt());
Set<Integer> integerSet = new LinkedHashSet<>(al1);
integerSet.addAll(al2);
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(integerSet);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
Output
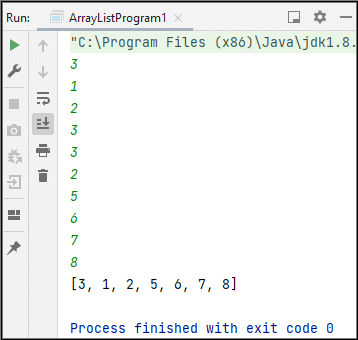
Thus, in this way, we learn how to merge and sort array list elements.
